Overview
In this module, you will learn what stereotypes, prejudices, microaggressions, and hate crimes are. You will also consider the impact they have on an individual’s experiences within the education system and society in general.
The module consists of:
- Concepts — key learning ideas
- Reflections — questions that ask you to reflect on your own experiences
- Practice — ways to apply the key learning ideas
- Learn about stereotypes, prejudices, microaggressions, and hate crimes.
- Understand the impacts of stereotypes, prejudices, microaggressions and hate crimes within the education system
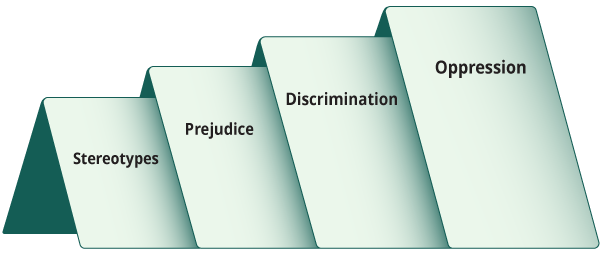
Steps Leading to Oppression
Sometimes people are aware of their own biases, and sometimes they are not. People can often make judgments about others without even realizing they are doing it.
Some teachers at my school hold biases and stereotypes of students from a different race; people don’t distinguish Asians from one another. They are not aware of some culturally sensitive topics and talk about them as if they know best… the stereotypes that Asians are really good at math, all they care about is good grades.
Student, Minister’s Anti-Racism Youth Dialogue Series, 2022
A stereotype is a generalization, or assumption imposed on a group of people, community, nation etc., based on very little evidence or experience.
Prejudice is a judgement or negative idea about a person or community based on stereotypes that are held about them. Prejudice is without sound rationale and reflects a lack of understanding.
Discrimination is when prejudice is acted upon towards an individual or group. This action consciously excludes, isolates, treats differently, or deprives another individual or group of their rights because of characteristics such as race, age, sex, ethnic origin, or ability.
Oppression is when a dominant group holds power and privilege that combine to bring about discrimination. Oppression results in unjust experiences and discrimination across a society. Oppression can be present in systems or institutions, such as in the media, medical systems, or education systems. Oppression leads to certain groups controlling and having power over others, which reinforces inequity.
Stereotypes, prejudice, and discrimination can build to oppression:
- Believing in stereotypes can lead to prejudice
- Acting on prejudices can lead to discrimination
- Discrimination is a form of power that can result in oppression
There are many types of oppression that operate in society, including racism.
Becoming anti-racist involves developing a clear understanding of oppression and how it reinforces racism over time. Understanding oppression is a key factor in being able to identify and validate the lived and living experiences of those who face it.
